Pressure Booster Accessory
Uson pressure booster offers a safe, quiet and cost-effective alternative to renting gas bottles or buying a clean, high-pressure, motor-driven...
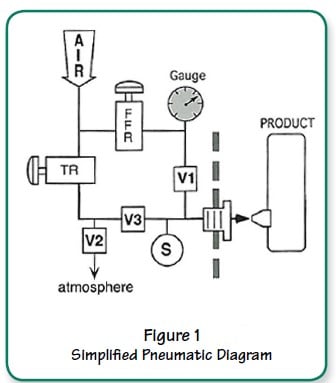
One of the most challenging tasks facing production and test engineers is how to quickly detect leaks in products that have a large volume (typically greater than 1 liter). Most large products must be filled with air rapidly to decrease the total test time. Testing throughput (the number of parts produced per hour) is nearly always a concern in manufacturing. Standard leak testers often do not have the ability to rapidly fill products under test with a separate air circuit and with the needed pressure, time and programmable limit controls.
The tester detects leaks in large products using pressure decay analysis. It has the speed, resolution, and repeatability to measure even small pressure changes in large products. The fast-fill option pressurizes product for a very short time at a pressure higher than normal test pressure. The fast-fill circuit bypasses the test circuit to allow much faster product inflation. The fast-fill option allows large products to reach test pressure much faster than would be possible using the standard test pressure for inflation. Yet, filling can be controlled to prevent the product from being subjected to excessive pressure.
The Fast-Fill option works like this:
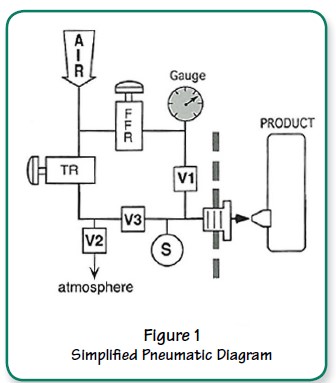
Figure 2 shows an example of a normal test cycle with fill, stabilization, test and dump times. Test pressure is typically reached before the end of fi ll time. Fill time must be set long enough to completely inflate the product and reach test pressure.
Fast-Fill
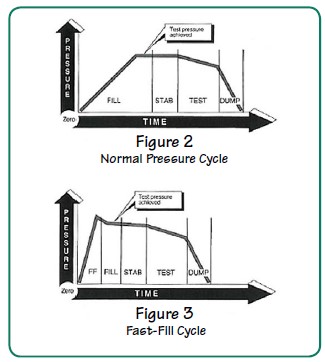
Figure 3 shows an example of a test cycle when using the fast-fill option. Fast-fill time precedes the fill time in the timing sequence. Test pressure is typically achieved during fill time with a slight overshoot during the fast-fill period.
The length of fast-fill time, together with the fast-fill pressure setting, determines the amount of pressure the product will be subjected to before the tester enters the normal fill time. As shown in the two timing diagrams, the same product can be tested in less time when using the fast-fill option.
Use the fast-fill option when the volume of the product is large and the test pressure must be held quite low. This applies to either rigid or flexible devices (typically molded plastic) that cannot be subjected to high test pressures.
The fast-fill option is also useful when testing large products even when the test pressure can remain high. Fast-fill inflates the product to the test pressure faster than filling through the tester’s normal test circuit.
To pre-stress a part prior to testing, fast-fill pressure and fast-fill times can be set to over-pressurize the product under test. Stressing is sometimes used to reduce inflation effects on a complaint part. In this way, testing is conducted on the flexible part after it has relaxed.
Uson pressure booster offers a safe, quiet and cost-effective alternative to renting gas bottles or buying a clean, high-pressure, motor-driven...
The Sprint iQ bidirectional check valve tester is equipped with a precision flow control and two pressure sensors.
Test the integrity of the cylinder head water jacket for porosity, while simultaneously testing each oil drain-back hole for casting blockage.
Industries